Coaxial Cables may not be something you get very excited about, but they are kind of important. In the world of communication and data transfer, they have earned themselves quite a name. In this article, you will find all the basic information about coaxial cables popularly referred to as coax. The article will explain the technical topics in simple words keeping in mind the beginners.
Everything You Need To Know about Coaxial Cables Design, Types, Applications, Pros, and Cons.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are Coaxial Cables?

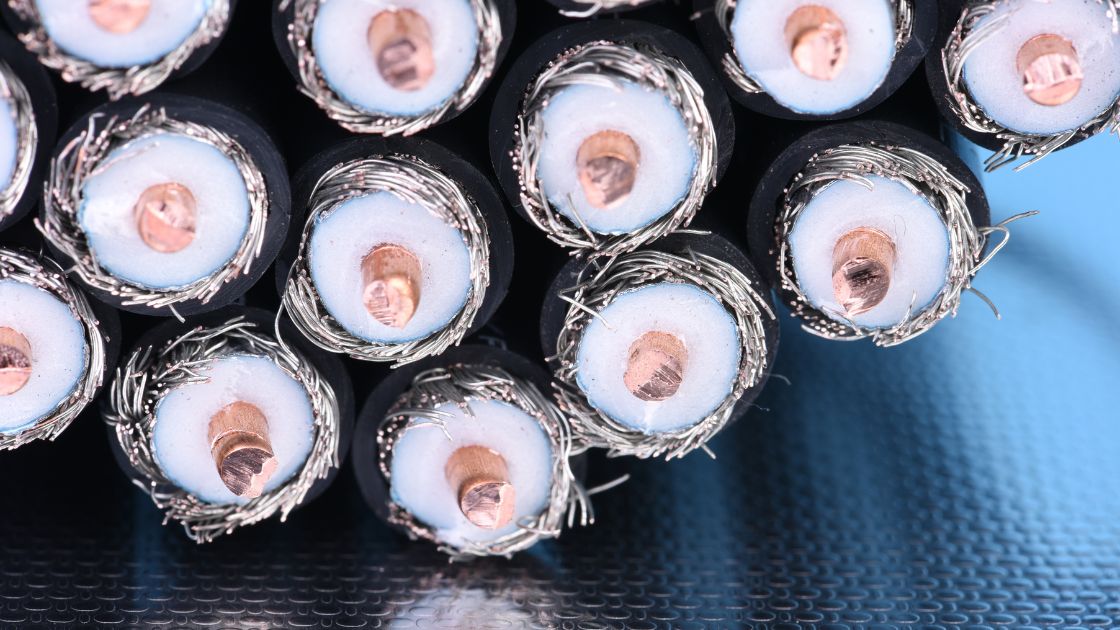
Coaxial cables is a popular choice for delivering high-frequency electrical signals over distances with low signal loss. Coaxial Cables are specially designed to prevent electromagnetic interference EMI, making possible data transmission over longer distances reliably. This is achieved by a geometric axis shared by an inner and outer core of the cable. This feature of the shared axis is the reason these cables are called coaxial cables.
Design of coaxial cables
Coax has two basic components innecr core conductor made of metal and outer layers for shielding and insulation.
- The central conductor is a solid copper or copper-clad-steel is wrapped into a non-conductive dielectric insulating sheath.
- To reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) this sheath is further wrapped by conducting foil shield/s and/or copper braid/s that form the outer conductor.
- In a standard design a PVC jacket encapsulated this structure and protects the cable from environmental factors that can otherwise damege the cable.

At the far ends of cable connectors are installed that function to plug the cable into devices.
How Signal are transferred in Coaxial cable?
The energy in one form or other is sent through wires using conducting materials. When this energy is introduced to the conducting wire, its electrons absorb the energy and get excited, this excitement generates a motion. These movements cause the transmission of electric signals.
Impedance: When an electric current is sent through a wire or cable using metallic conducts like copper, some of the energy is lost in the form of heat produced due to internal resistance. This resistance is called impedance. Coaxial Cables are most frequently divided on the basis of their impedance.
- Mostly cables used in data and wireless communication have 50 Ohm impedance. These cables have applications in two-way communication systems, RF & Microwave transmissions, data transmission, and M&C applications.
- Video signal transmission requires a nominal impedance of 75 ohms.
Another form of loss of energy or signal strength is formation of electromagnatic field. Electrons get excited during conduction and jump from one energy level to the other. During this process, electromagnetic radiation with a varying range of frequency, the wavelength is emitted.
This loss of energy can decrease the signal strength, and is called signal leakage. Coax is designed in the form that insulating sheets can prevent the conduction of energy to the outside environment and hence reduce the signal leakage. Therefore insulating dielectric layers help in transmission of good quality signals over the distance.
This insulating dielectric layer also prevents electromagnetic waves in the surrounding to seep into the cable network and interferes with signals flowing in the cable. This electro magnetic interference (EMI) is sometimes also called cross-talk or noise. Reduction in EMI is also a quality of coax that make them a more suitable option in comparison to twisted pair.
Coaxial cables can either have foil shielding or braided shielding in the layering for insulation. Foil shielding is usually aluminium sheets and protects against higher frequency EMI. Braided shielding provides the best protection against lower frequency EMI. But even the best shielding can not give hundred per cent resilience against EMI or leakage, and there is a signal loss to some degree as the signal travels over the distance.
The amount of signal loss is an important factor when you are looking to buy a coax. Depending upon your need you need to keep in mind the signal loss over the distance unit.
Applications of Coaxial Cables
They were patented in 1880 and since then have found many many applications.
- These cables are used to transfer video, voice signals, and audio data in the internet sector and telecommunication field.
- They are a standard part of several common assemblies like telephone trunk lines, cable television signals, and cell phone boosters.
- In your homes, you use these cables for DVD players and other types of media devices to our televisions and display devices.
- They are sometimes also used for networking and ethernet connection, however twisted pair or optical fiber is more frequently used for this purpose.
Different types of Coaxial Cables

Coax are of several types differentiated on the basis of design, sizes and lengths, based on specific application.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Coaxial Cable
Coax is used instead of twisted-pair cables and even more modern optic fibers. The decision is made based on the requirement of application considering the pros and cons of coax cables.
Pros
These cables offer a better quality of signals in comparison to twisted pair cables and are capable of transmitting a wider range of frequencies relatively. When compared to fiber optics the signal quality is nearly the same but coax are easier to install, definitely much durable, and less costly. Thus coax have bellow mentioned merits:
- Reduction in interference
- High Bandwidth levels
- Higher transmission capacity
- Better Insulation
- Easy Installation
- Durable
- Low-Cost maintainance
Cons
Some of the reasons coax is not preferred in comparison to more costly optic fibers is due to significant data loss over the extended distance, signal leakage at the point of connection at the ends where the connector is installed. Since a splitter can be installed at any point of cable, unauthorized usage of data is also a significant security issue. Therefore coaxial cable has the following demerits.
- Signal Leakage at the point of connection
- Poor long distance transmission
- Security issues due to unauthorised acess
Different Types of Coaxial Cables
Most frequently you would come across two types of coaxial cables, one prefixed with RG and the other prefixed with RF. RG “Radio Guide” was a military standard of how thick the cable was. Following are the most commonly used coaxial cable types:
RG-6 – overall thin cables with larger conductors for better signal transmission and thicker dielectric insulation for more effective transmission of GHz signals.
RG-59 – thin cables with a thinner central conductor. Due to smaller diameter they are perfect for going through the walls and ceilings and thus more suitable for domestic application as .
RG-11 – is thicker with lower attenuation levels, which means it is more suitable for transmission for a longer distance.