As the cities are growing and the trend of urbanization is becoming larger day by day the major factor towards air pollution is car pollution or vehicular pollution. The vehicular emissions or car pollutants harm our health and contain greenhouse gases that contribute to air quality disruption and smog formation. Burning gasoline and diesel fuel creates harmful byproducts like nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, benzene, and formaldehyde. In addition, vehicles emit carbon dioxide, the most common human-caused greenhouse gas.
What is Car Pollution and smog?
Car Pollution
When gasoline and diesel get burned by vehicles, the exhaust from the chimney duct contains toxic pollutants including carbon monoxide, smog-causing volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxides, formaldehyde and benzene. The main pollutant of the environment from automobile exhaust is CO, carbon monoxide.
Smog Formation
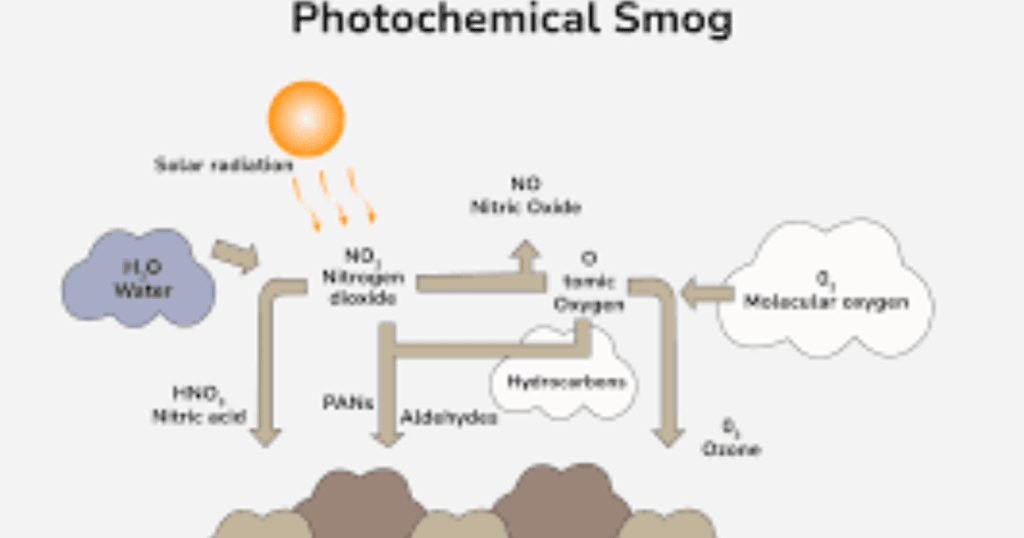
The type of air pollution forms when certain air pollutants react with sunlight. The process is more likely to occur on hot, sunny days with more intense solar radiation. The process is known as smog formation. Smog is formed when:
- Pollutants are released: Pollutants like nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are released into the air from vehicles, factories, and other industrial activities.
- Sunlight reacts with pollutants: The pollutants react with sunlight in a series of chemical reactions. That is called photochemical smog.
- Secondary pollutants are created: The reactions create secondary pollutants, like ground-level ozone, which is a key component of smog.
Sources of Car Pollution
Automobile pollution or car pollution primarily comes from the emissions produced by vehicle exhausts. In urban areas it is common to witness cars emitting clouds of white or black smoke, contributing to air and noise pollution. When a ton of gasoline is combusted in an automobile engine, it releases between 10 to 70 kilograms of exhaust gases, containing 150 to 200 different compounds. In addition to these gases, the fuel and combustion systems can leak about 20kg to 40kg of gasoline and gas, further adding to the environmental burden. These emissions include harmful gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides and particulates such as lead dust and carbon black, which degrade air quality and pose serious health risks.
Correlation b/w Car Pollution and Smog Formation
Yes, there is a visible correlation between car pollution and smog formation. Cars and other vehicles release emissions that contribute to smog which contains a mixture of pollutants. Cars release emissions like nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons when fuel is burned in the engine. When sunlight hits these emissions, they undergo photochemical reactions that create ozone. Ground-level ozoneOzone is a harmful pollutant that reacts with other chemicals in the air to form smog. Smog is a complex process that can be exacerbated by weather conditions and urban topography.
The correlation between vehicular or car pollution and smog formation is the emission of pollutants from vehicles to form ground-level ozone. The cars and trucks contribute to smog by emitting pollutants that react to form ground-level ozone. This process is called photochemical smog.
Types of Car Pollution
Car pollution comes in several forms, and each has its own impact on the environment and our health:
- Carbon Monoxide: This is a gas that forms when fossil fuels are burned, and cars are the biggest contributors to carbon monoxide emissions. It’s colorless and odorless, but it can be harmful when inhaled in large amounts.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Produced during combustion, NOx is a highly reactive gas that can lead to the formation of smog when it reacts with other chemicals in the air. It’s one of the key contributors to air pollution in cities.
- Particulate Matter (PM): This includes tiny particles like soot from car exhaust. These fine particles can penetrate deep into your lungs and cause serious health problems, especially with prolonged exposure.
- Hydrocarbons: These are released when gasoline and diesel are burned. They can also evaporate from fuel tanks, especially in warmer climates, contributing to air pollution.
- Ozone (O3): Not directly emitted by cars, ozone forms when nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds mix with sunlight and heat. While ozone is good in the upper atmosphere, ground-level ozone can lead to breathing problems, worsen asthma, and even increase the risk of stroke.
Impacts of Car Pollution and Smog
The impacts of car pollution are widespread on health, the environment, and finances
Production and destruction
Car production takes a major share on open roads. As people rely on personal transport it releases more pollutants in the air. Similarly, the end of a car’s life doesn’t mark the end of its environmental impact. Plastics, toxic battery acids, and other products may stay in the environment. Fortunately, junkyard pile-ups are becoming much smaller than they were in the past. About three-quarters of today’s average car, including the bulk of a steel frame, can be recycled.
Production, recycling, and disposal costs to the environment are difficult to quantify and largely beyond the control of most consumers. It’s also true that most of an automobile’s environmental impact, perhaps 80 to 90 percent, will be due to fuel consumption and emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases. The petroleum products are a big red flag raiser because their extraction and burning is an extensive process damaging the natural ecosystem. Also contributes to environmental disasters such as oil spills. We need fuel-efficient and less impactful procedures to be followed to become less hazardous.
Air quality
Vehicles are Pakistan’s biggest air quality compromisers, producing most of Pakistan’s air pollution. The smog, carbon monoxide, and other toxins released by cars are especially troubling because they leave exhaust pipes at street level, where humans breathe the polluted air directly into their lungs. That can make auto emissions an even more immediate health concern than toxins emitted high in the sky by industrial smokestacks.
Infrastructure
The infrastructure is an associated impact of car pollution as the building of roads to support them. This issue can be difficult to tackle from other factors, such as population growth and resource consumption. Still, it is also not easily addressed by technological advancements like fuel efficiency and electric propulsion. Road building has a big impact on emissions and wildlife.
Mitigation Measures of Car Pollution and Smog
1. Car pollution and smog in Pakistan can be mitigated by driving l and using more fuel-efficient vehicles.
2. Vehicle maintenance by:
- Keeping your car in good repair.
- Avoid overloading your vehicle, especially diesel vehicles.
- Convert your vehicle to compressed natural gas (CNG).
- Plant trees and cover open spaces with grass
- Plant and care for trees.
- :Other measures
- Take extra precautions during construction to avoid dust generation
- Limit outdoor activities during smoggy days
- Wear masks when going outside
- Stay informed about local air quality levels
- Drink plenty of water to keep your respiratory system hydrated
Conclusion
In the end, it is gathered that with small individual steps we can make a change and reduce smog effects. We can use public transport and also can use energy-efficient vehicles and electric power vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is car pollution?
2. What is smog?
3. What is the correlation between car pollution and smog?
4. Enlist some mitigation measures for car pollution and smog?
2. Fuel conversion from diesel and gasoline to Compress Natural Gas(CNG).
3. Other measures include:
Take extra precautions during construction to avoid dust generation
Limit outdoor activities during smoggy days
Wear masks when going outside
Stay informed about local air quality levels
Drink plenty of water to keep your respiratory system hydrated.
5. What are the types of car pollution?
Carbon Monoxide: This is a gas that forms when fossil fuels are burned, and cars are the biggest contributors to carbon monoxide emissions. It’s colorless and odorless, but it can be harmful when inhaled in large amounts.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Produced during combustion, NOx is a highly reactive gas that can lead to the formation of smog when it reacts with other chemicals in the air. It’s one of the key contributors to air pollution in cities.
Particulate Matter (PM): This includes tiny particles like soot from car exhaust. These fine particles can penetrate deep into your lungs and cause serious health problems, especially with prolonged exposure.
Hydrocarbons: These are released when gasoline and diesel are burned. They can also evaporate from fuel tanks, especially in warmer climates, contributing to air pollution.
Ozone (O3): Not directly emitted by cars, ozone forms when nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds mix with sunlight and heat. While ozone is good in the upper atmosphere, ground-level ozone can lead to breathing problems, worsen asthma, and even increase the risk of stroke.