This article will explain the types of network cables including Coaxial cables, UTP STP twisted pair, and SMF MMF fiber, and their different specifications
What is networking?
When two or more devices are connected using wires or cables for sharing data, this is called networking.
What are network cables?
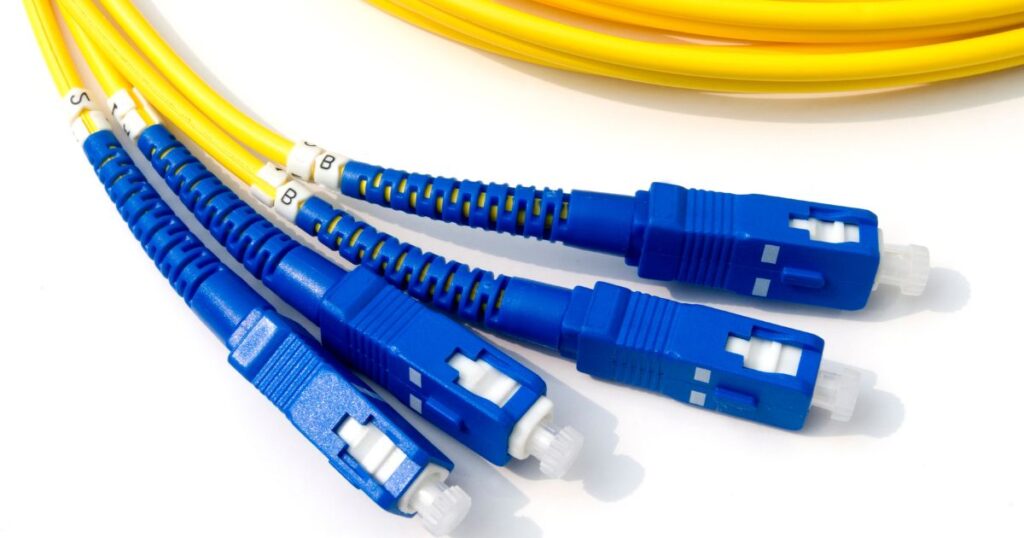

In some networks only one type of cable is used to connect the devices while in other cases more than one type of cable can be used within the same network.
What are Different Types of Network Cables?
Popular types of network cables can be categorized into three groups
- Twisted pair (Shielded Twisted Pair STP and Unshielded Twisted Pair UTP)
- Coaxial Cables (Thicknet and Thinnet Ethernet)
- Fibre Optic
Types of Network Cables Explained
Coaxial Cables
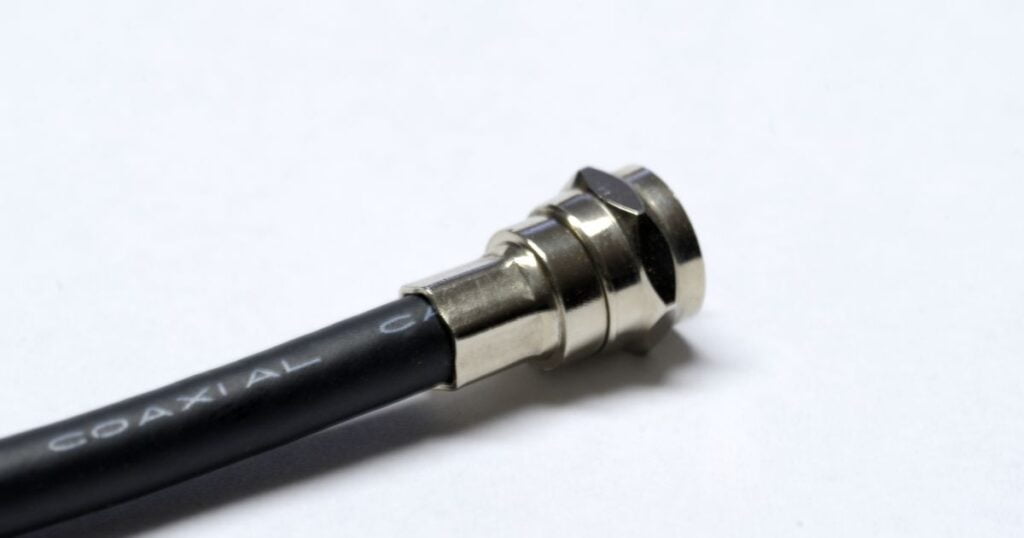

Although coaxial cables were not designed to serve computer networking, their low cost, EMI resistance, and durability made them a good candidate for networking cables during the ’80s and ’90s. Thicknet RG 58 and Thinnet RG 8 are no more used for ethernet connection but they still have application in other networking such as linear bus networks. RG 6, RG11, and RG 59 are used for cable networking, connecting TV sets, internet devices, and Cameras with the source of signals.
Twisted Pairs
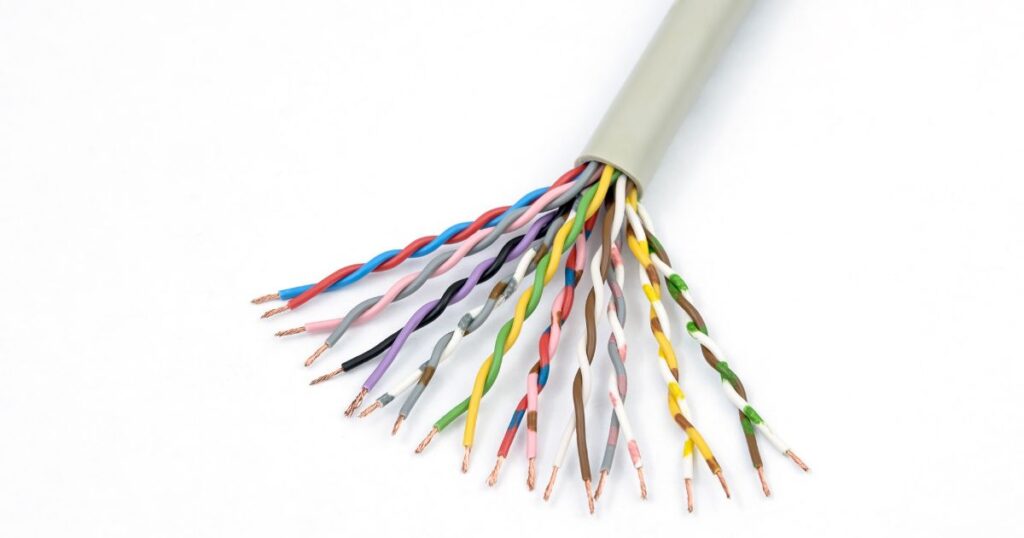

While the use of coaxial cables for internet networking is obsolete or minimum now, several upgrades have been introduced in a variety of twisted pair wires used for internet networking. UTP is extensively used in Ethernet or LAN s they are the lowest cost option. However, as they do not provide any protection against electromagnetic interference, in areas with a high probability of EMI or noise from the environment they are not suitable. STP is preferred over UTP in such situations.
Optic Fiber Cable
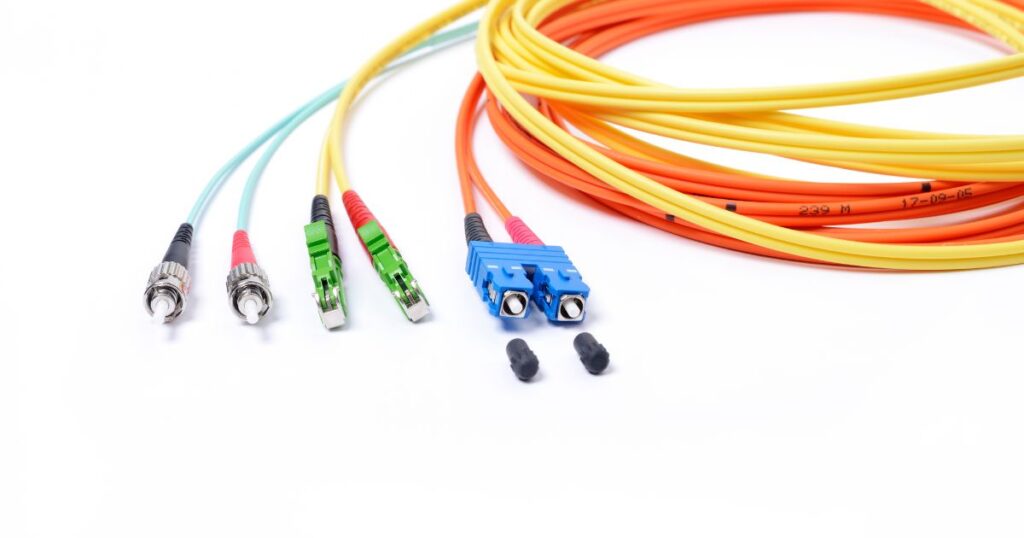

Fibre is the latest hardware for cable networking. These cables do not transfer data over copper wires in the form of pulses of electricity, instead, they contain optical fibers to carry data as light beams. A plastic coating protects each individual optical fiber which is further enclosed in a protective tube. This gives strong resistance to external interference making a super reliable, high-speed connection possible that has 26,000 times more transmission capacity than twisted-pair cables. However, this setup is also relatively expensive.
Specifications of Network Cables
Categories of Coaxial Cables used for Networking with Specifications
There are two types of coaxial cables used in networking:
- 10Base2 also called Thinnet can carry signals for up to 200meters
- 10Base5 also called as Thicknet can carry signals for up to 500meters
BNC connectors are the most commonly used types of coaxial connectors in networking although the size and specification of the connector may vary according to the cable used in the network.
Categories of UTP with Specifications
CAT1 Voice Only (Telephone Wire) for 1 Mbps speed
CAT3 10BaseT Ethernet for 16 Mbps speed
CAT4 Token Ring (Rarely used) for 20 Mbps speed
CAT5 100BaseT Ethernet (2 pair) for 100 Mbps speed and Gigabit Ethernet (4 pair) 1000 Mbps speed
CAT5e Gigabit Ethernet for 1,000Mbps speed
CAT6 Gigabit Ethernet for 10,000 Mbps speed
Categories of STP with Specifications
There are three different configurations of STP cable available:
- Each individual pair of wires is shielded with a foil.
- All wires are collectively wrapped as a group in a single foil or braid shield inside the jacket.
- Double shield twisted pair where each individual pair is wrapped in a shield and the entire group of wires is also covered by a shield.
Categories of Optical Fibre with Specifications
Fibre networks can be shared or dedicated and there are two types of fiber cables:
CAT2 LocalTalk & Telephone (Rarely used) for 4 Mbps speed
Singlemode SMF
It has a small core that lets only one mode of light to propagate at a time, which decreases the number of light reflections as the signals pass through the core. Due to this, it has lower attenuation and is able to transmit the data further and faster without much signal loss. The most common application is in telecom, and CATV networks.
Multimode MMF
It has a core with a larger diameter that allows for the propagation of multiple modes of light allowing a larger amount of data transmission. This causes to increase in the number of light reflections during signal transmission. Due to high signal dispersion, these cables have lower bandwidth, higher attenuation which means the further the signal is transmitted lower the signal quality gets. As these cables are not suitable for long-distance transmission their most common applications are LAN, security systems, and general fibre networks.