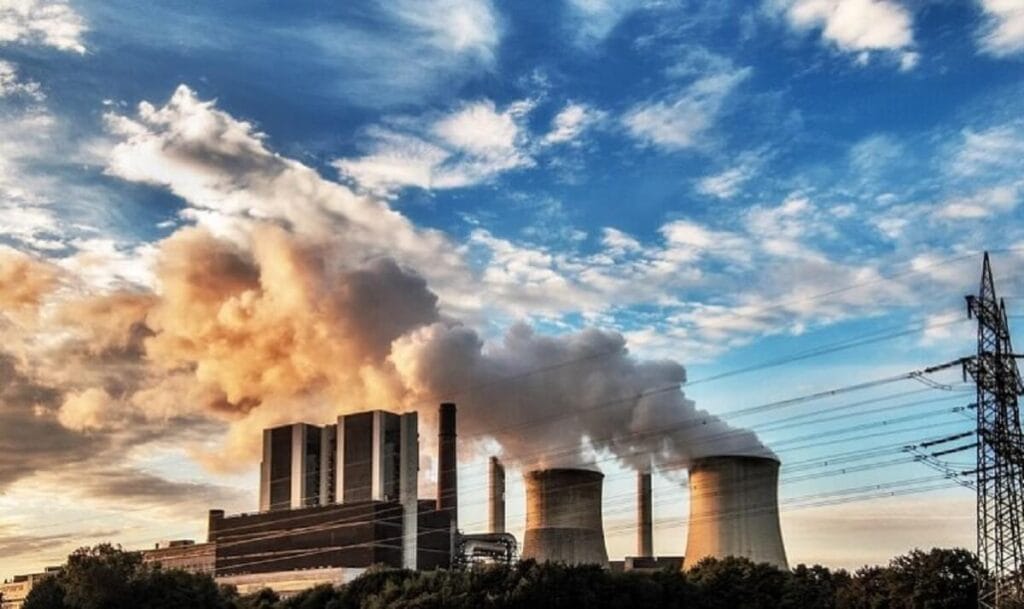
What is a smog?
The main issue these days in urban pollution is the smog. The combination of air pollutants and exhaust gases created by human activities and their interaction with sunlight is called smog. Smog in simple words is the mixture of smoke and fog in the atmosphere. The main causes of smog are human activities such as vehicular emissions, burning of fossil fuels, industrial activities, and some others.

Types of Smog
There are two main types of smog.
1. Photochemical smog
This type of smog is caused by the reaction of sunlight with pollutants in the atmosphere, such as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds. This smog is also known as the Los Angeles smog. It is very common in urban areas to have vehicular emissions from cars and other traffic vehicles. This type of smog includes the main causes of smog which is the atmosphere turning a light brownish color and can reduce visibility, damage plants, irritate the eyes, and cause respiratory problems.
2. Sulfurous smog
This type of smog is caused by high levels of sulfur oxides in the air. It is also as London smog. It is often thick and blackish and found in areas with a lot of industries. The main cause of sulfurous smog is the burning of sulfur-containing fossil fuels, especially coal.
Causes of Smog
8 causes of smog includes vehicular emissions, natural causes, industrial emissions, construction activities, burning of fossil fuels, natural causes , urbanization,poor regulatory measures and agricultural activities.
1. Vehicular Emissions
The primary pollutants are nitrogen oxides(NOx), carbon monoxide (COx), and volatile organic compounds(VOCs). The reaction of pollutants with sunlight forms ground-level ozone. The key contributing factor are high vehicle density in urban areas. It is the use of older, inefficient engines. The lack of proper vehicle maintenance also plays an important role. Some examples are urban centers like Los Angeles, Beijing, and New Delhi.
2. Industrial Emissions
Some of the major sources are factories, power plants, oil refineries, and chemical plants. The main pollutants released are Sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrous oxideNOₓ, and particulate matter (PM). These are generated through combustion, chemical reactions, and waste discharge. These include the main causes of smog, which impacts local and regional air quality standards.
3. Burning of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels come from electricity generation, residential heating, and transportation. The main pollutants include Sulfur dioxide from coal and oil and NOₓ from gas-powered engines. They play a key role in both sulfurous and photochemical Smog. The seasonal impact is the increased smog in winter due to heating demands.
4. Agricultural Activities

Burning crops releases particulate matter and carbon monoxide in the rural areas of Punjab, Pakistan. The use of fertilizers and pesticides results in the release of ammonia and other reactive compounds into the atmosphere. The livestock emissions such as methane release contribute to smog precursors.
5. Construction Activities
The sources of pollution here are dust and debris from construction sites. The use of construction materials like paints and solvents releases VOCs. The measures taken to suppress dust are inadequate.
6. Natural Causes
As the wildfire release massive quantities of smoke, carbon monoxide, and PM(particulate matter). The volcanic activity releases SO₂ emissions leading to sulfurous smog. The weather conditions such as temperature inversions trap pollutants. As the low wind speeds reduce dispersion.
7. Contribution of Urbanization
Population growth has increased energy and transportation demands. Also, urban heat islands are amplifying chemical reactions leading to smog formation.
8. Role of Poor Regulatory Measures

One of the major causes of smog is ineffective Environmental Laws. Also the weak enforcement of emission standards. A big cause of smog is the inadequate monitoring of Pollution Sources.
Conclusion
In the end, it is suggested that the causes of smog are interconnected in nature. As many factors overlap and amplify one another. There is a need for firm actions that are the framework of comprehensive mitigation strategies. It is to go hand in hand with government regulations, industries, and individuals in reducing the causes of smog.